One of the most significant crypto-related pillars is the growth of exchange platforms on which investors and crypto fanatics can trade and exchange cryptocurrency possessions on open markets. These exchange platforms are centralized or non-central. Because of the characteristic occurrence of third-party objects and dominant oversight, centrally managed exchange platforms are susceptible to SPOF (Single Point of Failure).
Moreover, to SPOF, which can happen caused of cooperated control by central authorities, the central exchange platform may also be the reason for rug pulling if the developers are deceitful and shaded. A diversity of security matters subsidizes the lack of centralized exchanges.
On the other side, decentralized exchanges (DEXes) are well-liked by frequent cryptocurrency enthusiasts and investors. The reason for this is nothing more than the assistance it delivers concerning the security of digital possessions. DEXes are platforms for exchange based on blockchain that imitate the security topographies and aspects of the blockchain that they’re constructed on. One example of these DEXes is Uniswap.
Uniswap’s Story
Uniswap was recognized in 2018 by Hayden Adams, a previous mechanical engineer employed by Siemens. Uniswap established its initial funding from VC companies Andreessen Horowitz, Union Square Ventures LLC, and Para Fi.
On November 2, 2018, Uniswap was publicly organized on the Ethereum mainnet. Uniswap stood out from other interactions in that it functioned on liquidity pools to swaps instead of running as the market maker.
Uniswap is a P2P exchange platform that lets users switch, trade, or exchange cryptocurrency without going through any third party. It originated on a permissionless blockchain and was hosted on the Ethereum platform – via smart contracts. It also has the native token UNI.
Since it is a decentralized platform based on Ethereum, Uniswap only cares about ERC-20 tokens, which are standard Ethereum-based tokens. UNI holders are the ones who oversee Uniswap without interference from any other third party. Having its token and being a DEX, Uniswap also signifies Automated Market Maker (AMM), which lets users trade on their liquidity pool.
One of the primary reasons for the repeated acceptance of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) is its stable growth over time; this has strained many pessimists and newcomers to the crypto-sphere. As DeFi produces by stretching its limbs and wings, criminals and mischief-makers are also looking for unlawful ways to income from DeFi customers and deceive users of their digital assets.
For example, Uniswap has recorded a trading capacity of nearly $1 trillion since its beginning on November 18, 2018. This, and more, make Uniswap the target of impostors to launch their fraudulent actions to fiddle innocent customers.
To avoid fraud on Uniswap, it is indispensable to know the kinds of scams that are most likely to be knowledgeable on Uniswap.
Is Uniswap Safe?
The Uniswap digital exchange has grown to become a tremendously used platform part of this movement. It proposes exchanges that swap Ethereum (ETH) in addition to other ERC-20 tokens and liquidity pools that earn money by placing tokens without the need for an intermediate centralized with cash. However, being among the top sought-after platforms within the DeFi ecosystem, Uniswap has become a prevalent victim of fraudsters. Although there are always dangers in the DeFi market, particularly given the number of hacks, Uniswap is harmless. If you are cautious and aware of scams, read the information in the following.
Decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap, Plasmaswap, and Sushiswap bid better autonomy in terms of self-custody and KYC or trading fees, as well as convenience to a new cryptocurrency; these exchanges necessitate more accountability, making it indispensable for users to know the kinds of scams obtainable and be aware of ominous signs previous to using the particular pool or tokens that are accessible and are presented on their platform.
Common Uniswap Scams: How to Identify and Avoid Scams
-
Rug Pulling Scam
A rug pull happens when developers shortly abandon the project and withdraw all of its liquidity. Pulling out liquidity is like eliminating the project’s funding and removing liquidity. Rug pulling is a term used to define DeFi projects that deliver essential liquidity to DEXes, such as Uniswap.
The newly launched tokens aren’t generally registered on central exchanges (CEXes), so they switch to DEXes which propose liquidity. Because Uniswap allows ERC-20 tokens to be used, ETH is provided as the liquidity for current projects as well as any new projects. Typically, when tickets are created, they have presented liquidity to DEX, where it was first launched.
The liquidity is joined with another cryptocurrency, such as ETH, in the occurrence of Uniswap. The new token may be accessible via an Original DEX Offering (IDO), where buyers purchase tokens, and the incomes will be protected for a particular time.
When the project is extensively or honestly adopted so that the value of tokens is positive, the project’s cash flow will be obtainable for the project’s inventor. To rug pull, developers can bid their tokens for the uppermost price, take from the project’s liquidity, or use dumps in intelligent contracts to trap depositors’ wealth.
Investors are now struggling to sell their tokens due to a lack of liquidity. They will likely find themselves forced to buy their tokens at the lowermost price due to an AMM pricing algorithm, which calculates fees for tokens concerning the coins in the pool for liquidity of DEX. Rug pulling is also the so-called “Liquidity pull” since pulling out the liquidity can lead to this type of scam.
-
Crypto Exit Scams
Exit scams are a deceitful technique undependable cryptocurrency developers employ to take depositors’ money before or after an ICO (Initial Coin Offering). A mainstream of new projects uses promoters or influencers to appeal to fans and investors to their schemes.
At first glance, the venture could seem genuine and without any dishonesty, either by promising high returns or even producing unbelievable results.
After the project’s launch, once developers have built faith, they will part from people’s possessions.
A good illustration can be originated in LoopX Crypto, which assured weekly revenue in its ICO. The company was recognized in September 2016. The company dragged its exit scheme in February 2018 after it elevated BTC and ETH to $4.5 million from its investors. Confido, Bitconnect, and numerous others also did parallel things.
-
Meme Coins Scam
Meme coins are cryptocurrencies constructed on memes or jokes on the Internet and social networks. They aren’t counterfeit coins; however, they promise their owners enormous revenues in the shortest period. They are tremendously unpredictable because they’re incredibly community-driven coins, i.e., their values are typically exaggerated by the corresponding public insights of their online communities and social media. This usually causes growth in FOMO.
In light of the actions of meme currencies like DOGE or Shiba Inu Other memes, coins have been prosperous, with the mainstream pulling on depositors. A good example is SQUID, which resulted from the well-known Squid Game TV series. However, it was a tragedy, so its value plunged by over 99 percent, and owners could not trade their tokens.
-
Mimicked or Fake Token Scam
This type of fraud committed on Uniswap happens when scammers determine an incorrect token waiting to be recorded and then create an account that’s like the official citation.
This type of fraud usually happens when scammers trick people into believing that famous preceding it. The fake listing is possible since scammers exploit the competencies of DEXEes such as Uniswap, which are open and license-free token citations.
Swindlers can trick crypto depositors into buying fake tokens and believing they are honest. The result is that fatalities are left with unusable tokens. A fake Teller financial token was presented in 2020, as was Acala, along with NEAR tokens. However, those who participated in them were counseled by genuine projects to stay away from them.
-
Social Engineering or Catfishing Scam
Persuasive entities are buying a specific token that may be fake. It can occur when the swindlers have access to their contact addresses. They’ll start any transaction and present it as if a depositor has bought the token, and they’re pinning their hopes on it. This generates attention that can drive people to take an interest in tickets, which could be incorrect or meme-like tokens.
Catfishing happens when a deceiver appears as somebody else through social media. Scammers may appear to be whales or projecting influencers and affect public belief about the token they want to use to create a means to deceive.
-
Swap Manipulation
One of the most current cryptocurrency scams contains manipulating the Uniswap swap feature. What is the apparatus behind this? It allows users to reach a separate receiver with a single click.
The feature permits users to offer a token to significant people. Making it appear that the influencer has participated in a particular token may increase the worth of the fake token. This makes it more striking to depositors.
-
Liquidity Pulls
Liquidity pulls are also called “rug pulls” and are dominant on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, where Ethereum (ETH) is attained from newly posted, and often in a hyperactive marketing operation. The purchase of tokens is brusquely taken away, preventing users from selling the newly developed tokens, thus recreating their investment.
These are false contracts designed to seem dependable. They are applied to make forced swap transactions seem genuine. Fake agreements are also employed to make false interchange reports.
-
Fake Contracts
Cryptocurrency contracts implement financial contracts. One of the most erudite crypto frauds is using fraudulent agreements.
How to Identify & Avoid Scams?
Before tapping your money in a bank, doing the required due diligence and examining for warning signals is critical.
Since users are becoming more careful concerning the pools and tokens they deal with, scammers have developed more advanced ways to bait users into giving their money.
One of the newest trends is to use sophisticated swap functions on DEXs like Uniswap and PlasmaSwap to make it seem like well-known community influencers have invested in a precise currency.
Research the Project
Although all pseudonymous or anonymous development teams must be measured as suspect -for occurrence, Bitcoin is a significant example in this regard — unless dependable sources back the unit. They should be preserved with caution as scammers are frequently unidentified or pseudonymous, and there is no way to distinguish between genuine and fraudulent actors.
If the team’s transparency is high, you should conduct suitable checks of their background to approve that their experiences, as well as their connections and experiences, are genuine and dependable. It is also significant to guarantee. The team only holds the most respected tokens presently in circulation. This is an ominous sign if they’re open regarding this or only transparent details are provided.
Check for Smart Contract and Code Audits
Honest schemes must have specialists check their smart contracts and codes to ensure no bugs can damage users. Audits can be expensive to accomplish. Therefore, the absence of auditing doesn’t mean the project isn’t genuine; however, as with all projects, they must be viewed carefully. You cannot distinguish between genuine projects that can’t afford the checking and scammers who don’t pay for them.
Verify Using Trusted Sources
Instead of searching for pairs or tokens on Uniswap, you can guarantee that you’re selecting reliable ones by mentioning a recognized source such as CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko crypto tracker websites. For occurrence, on CoinMarketCap, you can, for instance, look up the token, choose it, and then click on the trading pairs at the lower part section. Clicking the qualified team in the middle of Uniswap will transmit you to the authentic Uniswap page. It will also support you in evading deceitful tokens. You can also select on the top of the page to use MetaMask.
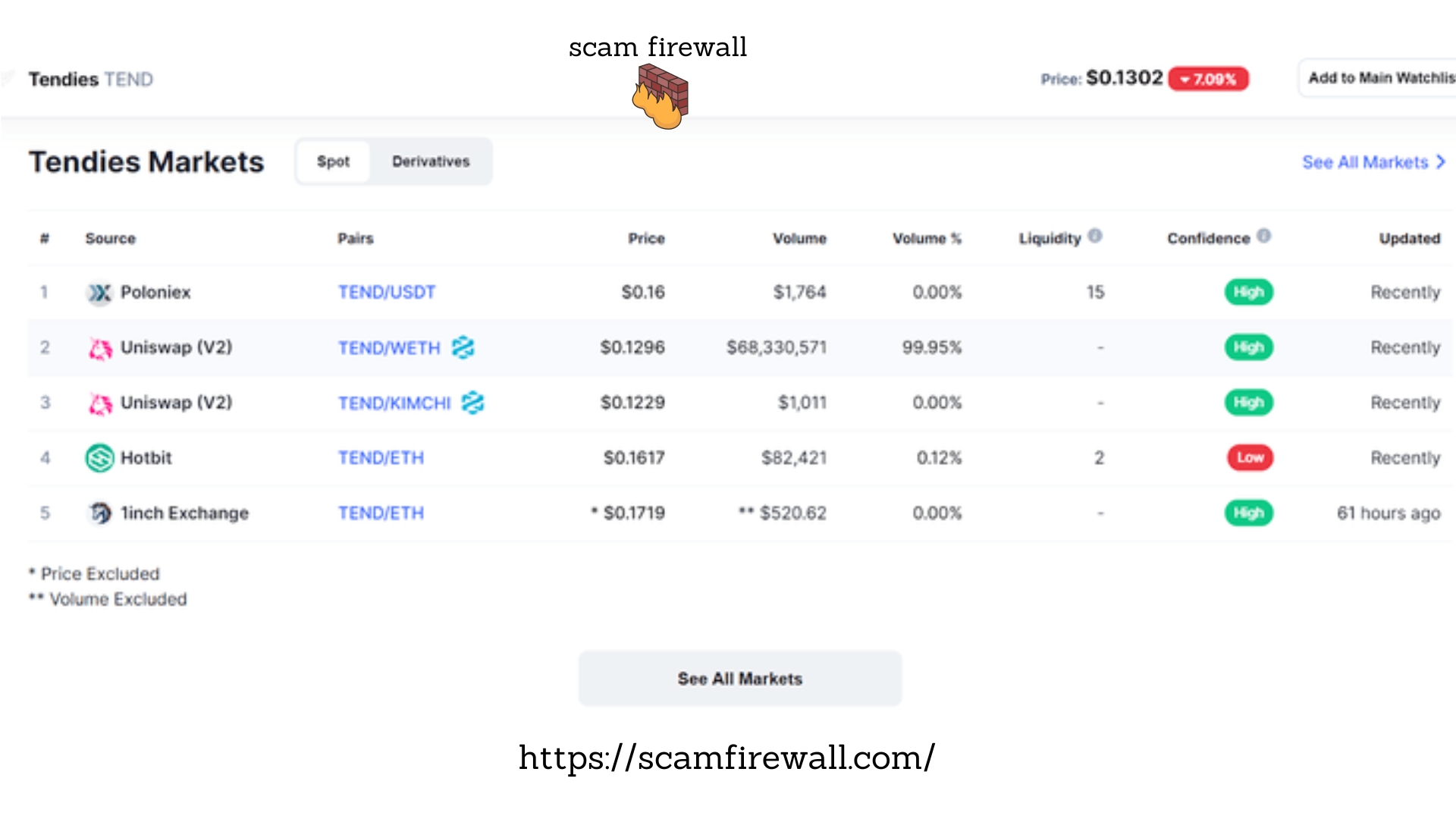
Because Uniswap’s procedure has no permissions and both bad and good performers can list tokens on it, it is common to get a notice for users to be practical to avoid fraudsters. Similar warnings are posted on PlasmaFinance Swap Page. These are suitable warnings in all cases; however, since the sign doesn’t seem for pairs that are more well-established from the same foundation, it could be used as a threatening signal. This isn’t to say that it’s essentially false. However, both bad and good actors aren’t always able to be distinguished, so caution should be trained.
You can also approve that it’s honest using Explorers such as Etherscan or Ethploler. Since explorers show every address, both good and bad, it’s critical to verify the legitimacy of a traditional source. On CoinMarketCap, it is easy to look for the name of the token, choose the decision of an Explorer from the pull-down menu on the right, then click it:
Analyze the Contract Address
Explorers like Etherscan can be exploited to confirm the crucial data essential to make an informed choice.
Check the total amount of liquidity in terms of quantity (24 hours), the number of transactions, when the last trade took place, and the date when the liquidity was either added or taken away. When any or all of the above numbers are small or unimportant, it could be a signal.
It is significant to also look into the address for the DEX contract with features like Uniswap and PlasmaSwap. Take a glimpse at total liquidity, volume, and recent transactions to regulate what is doubtful.
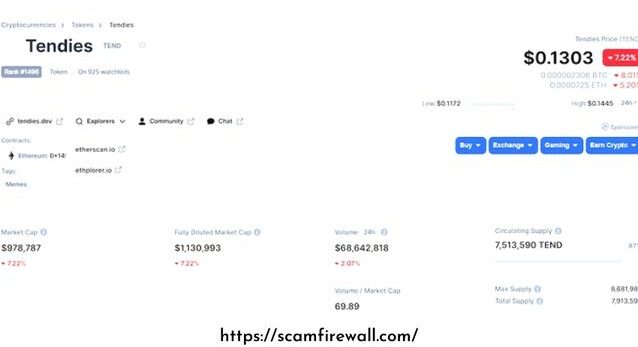
In our Tendies example, we detect that the pool is not as liquid and transactions, but it has a 24-hour rate similar to that of some of the most popular pairs on the Uniswap platform. Because Tendies isn’t a significant token (currently in the 1480th position on its market value on CMC), it may designate that it is overstated by wash trading to boost the pool’s volumes and to draw in traders to an enormously unliquid market. This shouldn’t be an astonishment because it was initially launched as meme-coin (self-styled as the “Dogecoin of the DeFi age”) that seems to have a considerable 4chan popularity.
Picture6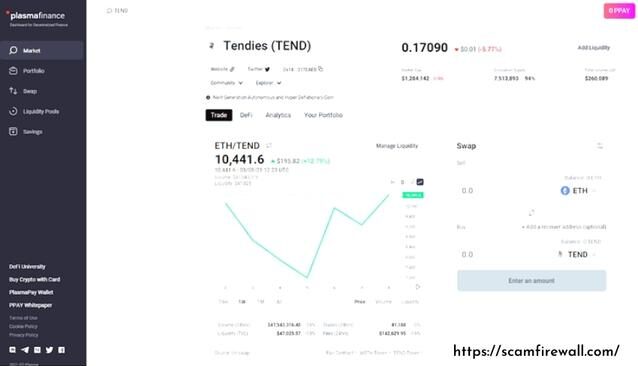
Whatever your feelings concerning DeFi’s sturdy ties to memes, and the speculation eagerness over specific tokens, it is significant to be careful about an indication of enormous volume. This can be confirmed by the comparatively small transactions linked to the same account. The remainder is smaller-value transactions.
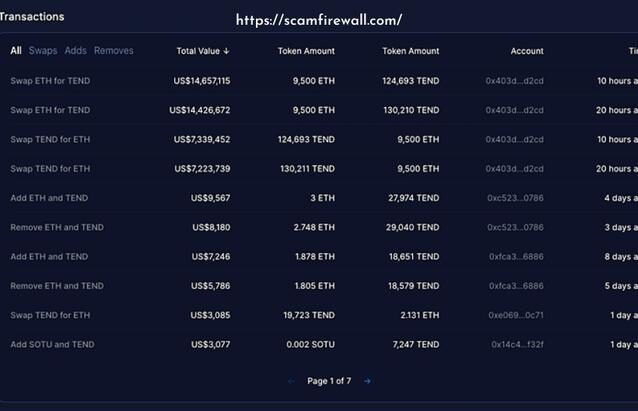
Investigate Social Media Accounts and Search Results
True projects with clear and exact plans will likely be present on social media platforms, showing good attendance, engagement with the community, and excellent reviews. The absence of token platforms in this feature could designate another warning sign.
It’s, therefore, worth checking out as you’re likely to find warning signs. Emphasis on the views of the general community, not on influencers that may be rewarded to promote firm tokens. Let’s take our Tendies occurrence, and it’s unlucky that there are worries regarding social media’s actions.
At the final point, these platforms, such as Uniswap, bid on various occasions to determine and earn supplementary earnings in the empire of financial devolution. However, as with all savings, you should conduct good research before concluding whether to avoid being intertwined with fraudsters. Suppose you’ve had some experience and time spent in the channels of crypto. In that case, you’ll obtain an aptitude to sniff doubtful projects, allowing you to narrow down the ones unaffected and with significant positive potential.